Strong Customer Authentication (SCA)
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a payment requirement mandated by the EU Revised Directive on Payment Services (PSD2) to enhance online payment security. It imposes two-factor authentication (2FA) during transactions, requiring proof of identity through at least two of the following factors:
- Knowledge – something the customer KNOWS (such as a password).
- Possession – something the customer HAS (such as a pre-registered smartphone).
- Inherence – something the customer IS (such as a fingerprint).
When does SCA apply?
SCA is applicable to online payments within the European Economic Area (EEA), with exemptions based on specific types of transactions.
In-scope transactions
The scope of SCA is determined by three factors:
- Geography: SCA is required when both the acquirer and issuer are within the EEA. However, if either is outside the EEA, SCA may still be applied. For example, if a customer uses an EEA card issuer and a merchant uses a non-EEA acquirer who supports SCA, the transaction will be authenticated and validated using SCA.
The customer's location does not impact SCA requirements. If a customer outside the EEA uses an EEA card issuer, SCA is still applied.
-
Payment method: SCA primarily targets customer-initiated transactions (CIT) made through online payment options, including credit/debit card payments, bank transfers, and digital wallets. Cleverbridge redirects customers to the respective applications for payments; therefore we can’t measure how these payment options might affect the customer experience.
-
Type of billing: One-time purchases, initial transactions and recurring payments for subscriptions require SCA.
Out-of-scope transactions
Relevant out-of-scope transactions are:
- Merchant-initiated transactions (MIT): Fixed and the variable payments initiated by the merchant on an agreed upon date with the customer consent are exempt.
- Inter-regional transactions: Transactions with an issuer or acquirer outside the EEA are exempt.
- Anonymous cards: Transactions using anonymous cards are exempt.
Exemptions
The following transactions are exempt:
-
Low-value transactions: Transactions below €30; those where the total amount attempted without SCA is under €100 or no more than five consecutive transactions without SCA.
-
Low-risk transactions (transaction risk analysis): This exemption is based on the issuer/acquirer fraud levels:
- Level 1: 0.13% for transactions below €100
- Level 2: 0.06% for transactions below €250
- Level 3: 0.01% for transactions below €500
-
Renewed subscriptions: Fixed-amount recurring transactions are exempt from the second transaction onwards.
Changes to the billing interval or the customer's payment details trigger SCA.
- Trusted beneficiaries: Customers can designate businesses on an accept-list of trusted beneficiaries. Accept-listed merchants are exempt from SCA.
- Secure corporate payments: Transactions initiated by legal entities, such as businesses, and processed through a secure dedicated payment protocol are exempt from SCA.
How is Cleverbridge managing SCA?
We assume responsibility for SCA compliance by:
- implementing a cardholder-initiated transactions (CIT)/merchant-initiated transactions (MIT) framework, and therefore making recurring transactions exempt from SCA.
- using an updated bank identification number (BIN) database to identify non-EEA issuer cards or anonymous cards, exempting them from SCA mandates.
- partnering with preferred acquirers with low fraud rates, which allows us to leverage TRA exemptions for transactions below €100.
We remain vigilant about changes in SCA exemption requirements and committed to ensure a seamless shopping experience for our customers.
3D Secure
3D Secure is an SCA-compliant authentication protocol for online card transactions. 3D Secure 2.0, the latest version, enhances the transaction process and boosts order conversion. Starting January 1, 2021, Cleverbridge will manage 3D Secure 2.0 authentication on hosted checkout pages for the EEA.
SCA flow (3D Secure)
In this SCA scenario for credit card transactions:
- The customer enters card details and clicks Next.
- After reviewing the payment information, they click Buy Now on the Cleverbridge hosted checkout page, initiating the SCA process.
First factor authentication:
- The card issuer sends an authentication request.
- The cardholder gets a push notification on their registered device. They open the notification, triggering the card issuer's app to open the authentication page.
- Reviewing details, the cardholder clicks Confirm, initiating the second factor authentication.
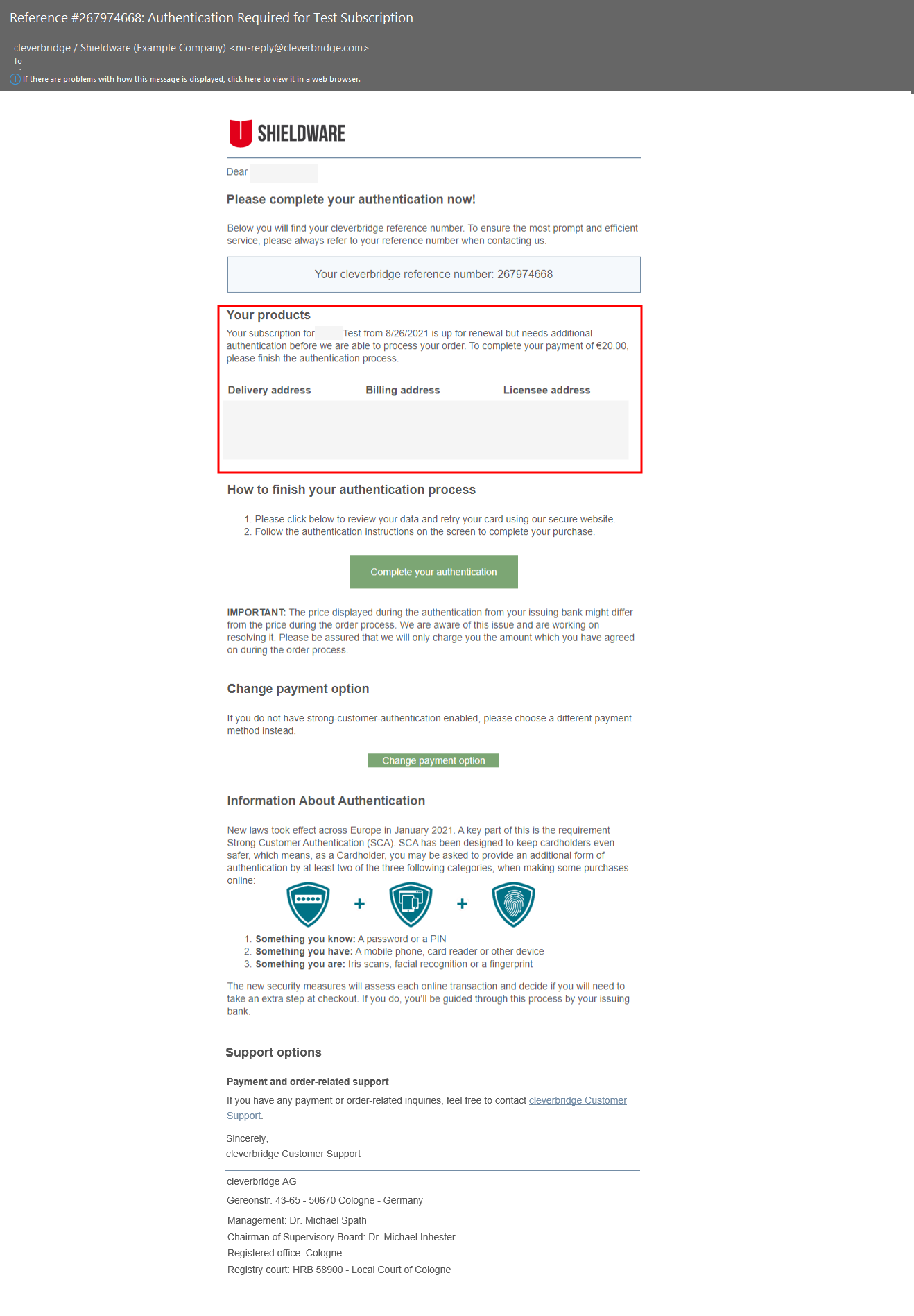
If the SCA flow is interrupted, the cardholder promptly receives a 3D-enrolled email from Cleverbridge, inviting them to complete authentication and offering product details. If the initial email is not acted upon, Cleverbridge sends a second email after 24 hours and a third email after 72 hours.
Both SCA emails, for one-time and recurring transactions, include vital information like product details, renewal date, and price.
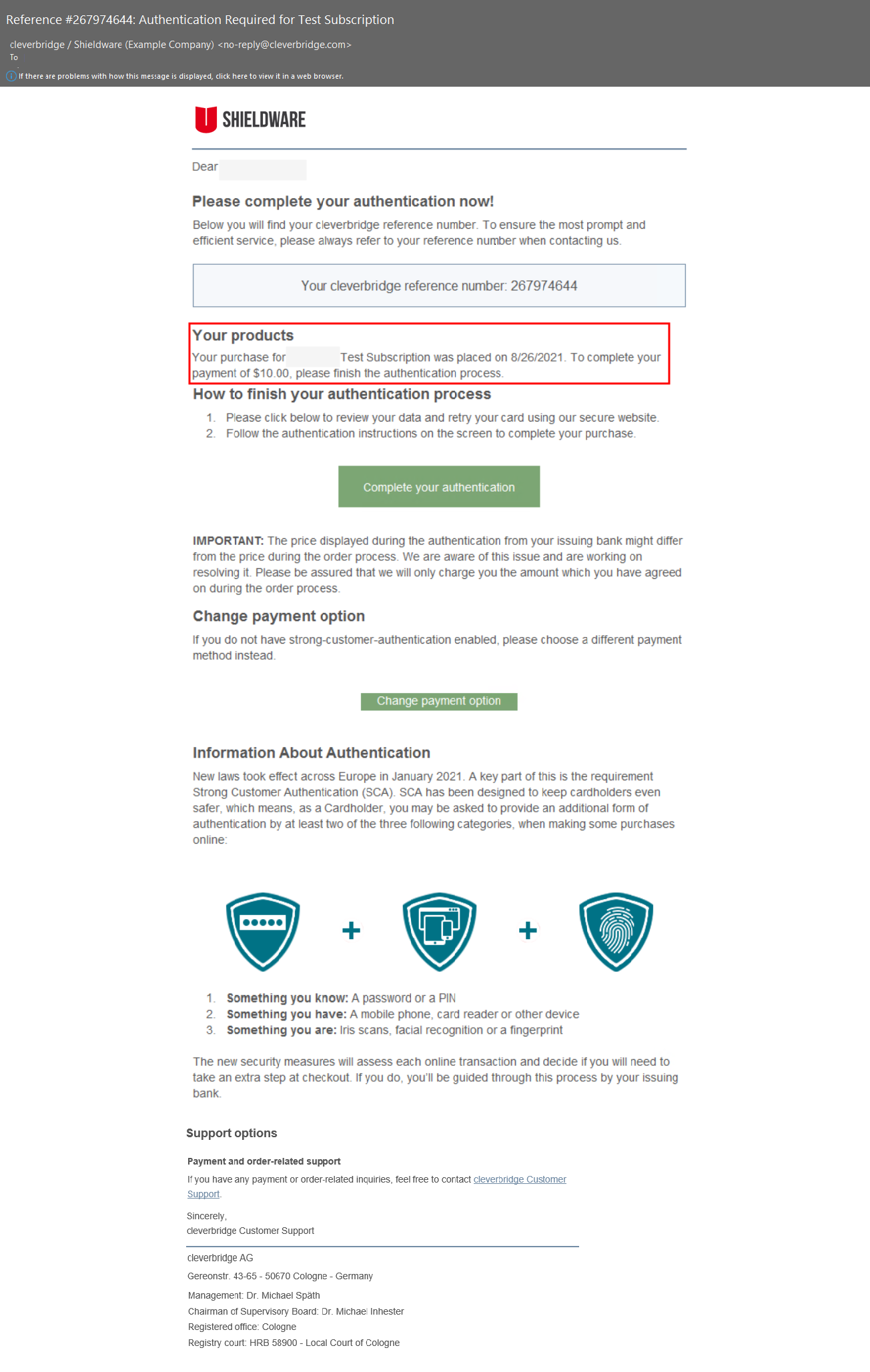
If a customer updates delivery, billing, or licensee contact during checkout, these changes are reflected in the SCA emails.
Second factor authentication:
- The cardholder receives a message notification on their device. Using the provided password, they authorize the payment.
- The registered device accepts the password, completing the SCA process.
- Customer views the Cleverbridge confirmation page in their browser.
For a detailed overview of the SCA process for credit/debit card payments, see the flow charts on the following pages: SCA for One-Time or Initial Transaction and SCA for Recurring Transactions.
FAQs
How will 3D Secure impact my checkout conversion?
The impact on conversion is uncertain as it depends on the cardholder's bank decision to challenge a transaction. However, the introduction of 3D Secure 2.0 aims to enhance the user experience and reduce friction in the checkout flow caused by authentication.
What happens with MITs when the original transaction was before December 31, 2020?
Cleverbridge will identify these transactions as merchant-initiated, aiming to exempt them from SCA upon renewal on or after December 31, 2020. SCA is still required if the customer initiates a payment method change for an active subscription.
With usage-based billing, is SCA required for each re-billing?
In most cases, subsequent charges for merchant-initiated transactions (MIT) do not require SCA, even if the amount varies. Cleverbridge ensures proper flagging of subsequent re-billings as MIT.
For merchant-initiated transactions, what happens if the transaction amount changes for subsequent transactions? Do they need SCA?
As long as the transaction is merchant-initiated and correctly flagged, subsequent transactions, regardless of amount changes, do not require SCA. Cleverbridge handles the flagging of subsequent re-billings as MIT.
How can customers accept-list merchants? Can this process be part of the checkout process?
The accept-listing process is not integrated into the checkout process. It occurs in the application or online banking system provided by the issuing bank, enabling customers to accept-list specific merchants.