Select a pricing model
Pricing models for digital products come in all shapes and sizes, depending on how customers want to use and pay for a product or service. Here is an overview of the four pricing models that the Cleverbridge platform supports, as well as some quick facts about them:
Pricing models
One-time charge pricing model
In the one-time charge pricing model, customers pay only once for the exact services rendered at the time of use. The customer pays before or after the service is provided. This pricing model is best for services that are delivered on demand, such as renting a movie online (payment before downloading a movie) or a ride with Uber (payment after the ride).
For an example of how you could leverage our platform to implement the one-time charge pricing model, see Example: One-time charge pricing.
Fixed pricing model
In the fixed pricing model, customers pay a flat fee for a service, such as streaming music. The fee is set for a billing interval and customers are billed upfront on a recurring basis, typically monthly or yearly. The fee can be linear (the same price for each billing interval) or variable (different price for each billing interval). Customers can change their level of service through an upgrade or downgrade. The fixed pricing model can be seen in services such as Apple Music and Netflix.
For an example of how you could leverage our platform to implement the fixed pricing model, see Example: Fixed pricing.
Seat-based pricing model
The seat-based (or user-based) pricing model allows you to define a price for your product per seat and for a specific time period, for example $20 per user per month. In this pricing model, your plan could define a minimum commitment of seats or you could allow a customer to add more seats at any time. You could also charge different amounts for different types of users, for example $10 per month for admin users and $5 per month for end users. The seat-based pricing model can be seen in products such as collaborative software or Dropbox for teams.
For an example of how you could leverage our platform to implement the seat-based pricing model, see Example: Seat-based pricing.
Usage-based pricing model
Under a usage-based pricing model, customers only pay for what they consume and they are normally charged for their usage on a monthly basis. In this pricing model, billing occurs after the consumption of the service, either on a fixed date, for example, the first day of the month, or on the anniversary of a customer’s sign-up date. The usage based pricing model can be seen in Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, and a mobile phone subscription billed according to the services you used.
For an example of how you could leverage our platform to implement the usage-based pricing model, see Example: Usage-based pricing.
Quick facts about pricing models
The following diagram presents categories of pricing models depending on two aspects: price scaling and billing cadence. Price scaling determines how many products or services a customer buys (seat-based) or how broad the level of the service is, for example separate tiers for basic, professional, and enterprise version (tier-based). Billing cadence defines when the product or service gets billed (one-time or recurring).
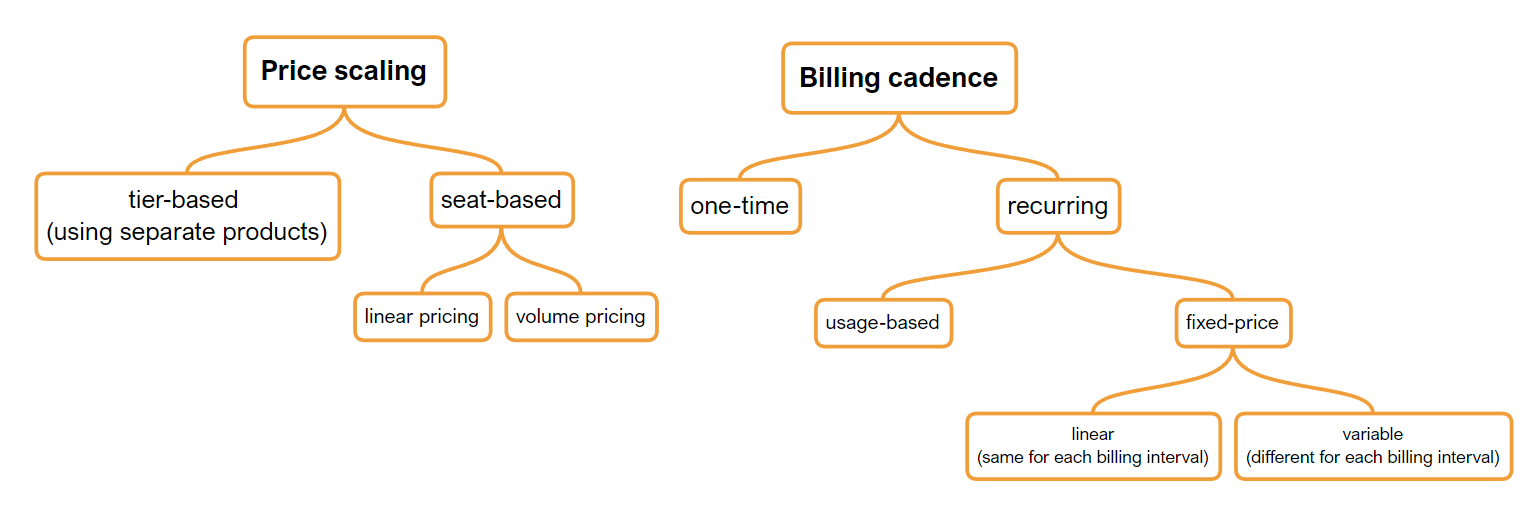
The two aspects are not mutually exclusive, and you can combine a recurring fixed-price product with seat-based pricing or a recurring usage-based product with seat-based pricing.
In addition to the four pricing models mentioned on this page, Cleverbridge also supports the tier-based model. If you would like to set a tier-based model, see Add billing plan selections.
Example: Fixed pricing
The following provides examples of how you could leverage the ecommerce platform to implement the fixed pricing model. In this use case, a fictional company, New Tunes, offers a music streaming service in which your customers are billed on a recurring basis, either monthly or yearly.
Example: One-time charge pricing
The following provides examples of how you could leverage the subscription commerce platform to implement the one-time charge pricing model. In this use case, a fictional client, Film Now, has a portal where customers can create an account on the Film Now website and then start to buy or rent movies using the Cleverbridge platform.
Example: Seat-based pricing
The following provides examples of how you could leverage the ecommerce platform to implement the seat-based (or user-based) pricing model. In this use case, Shieldware offers access to security software which customers pay for on a monthly basis. In their business model, the client charges 10 USD per month for every user.
Example: Usage-based pricing
The following provides examples of how you could leverage the ecommerce platform to implement the usage-based pricing model. In this use case, a fictional company, CloudBit, offers security scans for corporate networks. On the first of every month, CloudBit calculates how many scans they conducted during the prior period, and they use the ecommerce platform to charge their customers.